HomeBlogFood SafetyA scientific journal in the US...
A scientific journal in the USA publishes an important article on the hygienic properties of wood
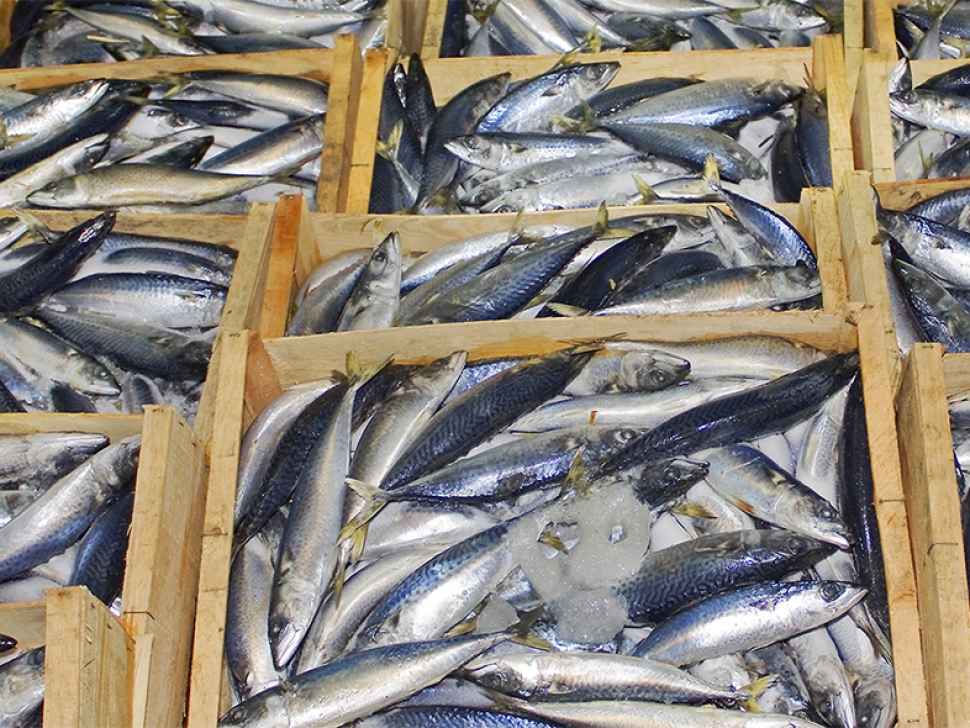
"Porous nature of wood, especially when compared to smooth surfaces, is not a limitation as far as hygiene is concerned, and that its microbiological status could even be an advantage."
It demonstrates that the porous nature of wood is not a limitation as far as hygiene is concerned, and that it even has the particular characteristic of containing antibacterial inhibitors of pathogens.
The prestigious scientific journal of the Institute of Food Technologists in Chicago (USA), “Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety” has published an article called: “Microbial Safety of Wood in Contact with Food: A Review” in its latest edition.
This study demonstrates that the porous nature of wood, especially when compared to smooth surfaces, is not a limitation as far as hygiene is concerned, and that its microbiological status could even be an advantage. In fact, its rough or porous surface often generates unfavourable conditions for the proliferation of microorganisms. Besides, wood has the particular characteristic of producing antibacterial components capable of inhibiting or limiting the growth of pathogenic microorganisms.
It is a critical review and summary of the scientific studies that have been carried out on wood and its contact with food, especially as far as microbiological behaviour is concerned.
It has been drawn up by a team of experts in France, Spain and Germany.
The article, which is based on a review of conclusions from scientific studies that have been carried out over the last 20 years, describes the general properties of wooden packaging and focuses on the microbiological status of natural wood.
The article goes on to discuss the parameters that influence the survival of microorganisms on wood. And it finally reports on the transfer of microorganisms between wood and food, in addition to the factors that influence this phenomenon.
This study demonstrates that the porous nature of wood, especially when compared to smooth surfaces, is not a limitation as far as hygiene is concerned, and that its microbiological status could even be an advantage. In fact, its rough or porous surface often generates unfavourable conditions for the proliferation of microorganisms. Besides, wood has the particular characteristic of producing antibacterial components capable of inhibiting or limiting the growth of pathogenic microorganisms.
The article can be consulted and shared by clicking on the following link: http://goo.gl/mmhHSu
Press release on the public consultation on the revision of the packaging directive
GROW Press release on the public consultation: Download
GROW responds to the EU’s public consultation on the revision of the packaging Directive
The aim of the consultation was to gather stakeholder input and improve packaging design to promote reuse and recycling, address over-packaging and reduce packa ...
Grow International Fruit Logistica 2020
The aim of the consultation was to gather stakeholder input and improve packaging design to promote reuse and recycling, address over-packaging and reduce packa ...
New evidence confirms the hygienic property of wood
Recent research carried out in France and Spain confirms once again the antibacterial properties of wood from black poplar and pine trees.At the beginning of l ...
A scientific journal in the USA publishes an important article on the hygienic properties of wood
A scientific journal in the USA publishes an important article on the hygienic properties of wood
It demonstrates that the porous nature of wood is not a limitation as far as hygiene is concerned, and that it even has the particular characteristic of containing antibacterial inhibitors of pathogens.
TECHNICAL MEETING 2017
March 29 2017, FEDEMCO hosted in Valencia the first technical meeting of GROW International this year.